Chapter 1
generations of computer
- Vacuum Tubes
- Transistors
- SSI/MSI circuits
- LSI/VLSI circuit
Components of CPU
- Register
- Control Unit
- ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit)
Components of hardware
- calculator
- memory
- controller
- I/O devices
BASIC FEATURE of Von Neumann : access memory by address and execute instruction in sequence
The operating system is appeared in the 3rd generation computers
Computer hardware consists of calculator, memory, controller and I/O devices.
System program: operating system, compiler, or utility program
machine language and assembly language can be implemented directly
The Art of Managing Complexity
-
Abstraction
-
Discipline
-
The Three-Y’s
–Hierarchy
–Modularity
–Regularity
Abstraction
- Hiding unimportant details
- Professionals handle professional issues
Discipline
Intentionally restrict for design choices
The Three-Y’s
-
Hierarchy(层次化)
A system divided into modules
-
Modularity(模块化)
Having well-defined functions and interfaces
-
Regularity(规整化)
Encouraging uniformity, so modules can be easily reused
The Digital Abstraction
Digital abstraction considers discrete subset of values.
- Focus on 0 and 1
- Ignore physical meanings
- make low level abstraction
The Analytical Engine
- Charles Babbage
- first digital computer
- Built from mechanical gears, where each gear represented a discrete value (0-9)
- Babbage died before it was finished
Number Systems
Decimal numbers
小数的表示

Binary numbers
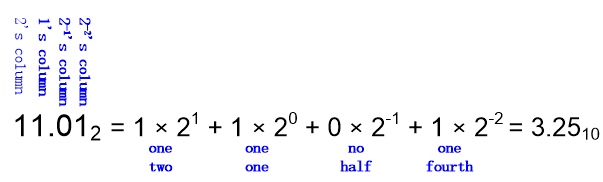
Hexadecimal numbers
(0~15) :0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F
Conversion


Bits, Bytes, Nibbles



Overflow
Overflow judgement
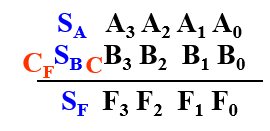
-
SA SB Sf
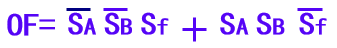
-
Cf C

-
double sign bit

Data types
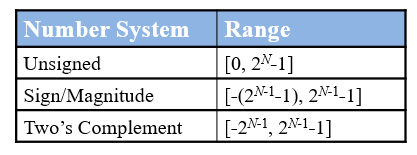

Signed Binary Numbers
•‘0’ for positive number
•‘1’ for negative number
•A separate sign bit is placed at msb position
Sign-Magnitude Numbers(原码)
+6 =0110
-6 =1110
-
Addition doesn’t work!!!
-
Two representations of 0 (± 0)
Range : 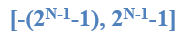
Two’s Complement Numbers(补码)
The most significant bit still indicates the sign (1 = negative, 0 = positive)
Range: 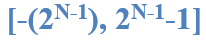
How to flip the sign?
1.Invert the bits
2.Add 1

补码转换成原码:首位是1,符号位不变,后面的取反之后加一;首位是0,不变
One’s complement representation(反码)
正数的反码是它本身,负数的反码符号位不变,其余取反
Increasing Bit Width
Sign-Extension
•Sign bit copied to msb’s
•Number value is same
Example
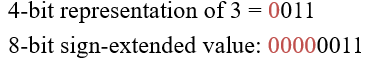
Zero-Extension
•Zeros copied to msb’s
•Value changes for negative numbers
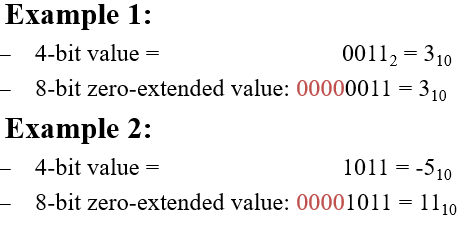
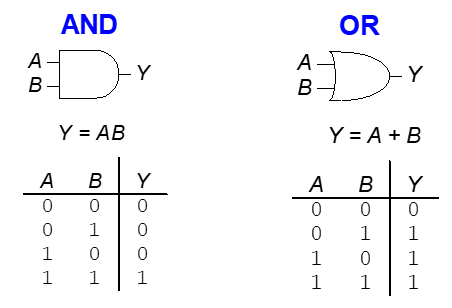
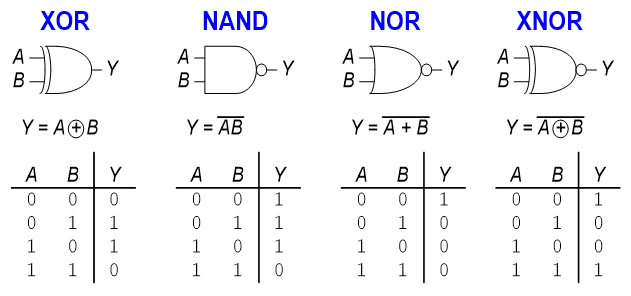
Logic Gates
Single-Input Logic Gates

Two-Input Logic Gates