Chapter 6
Introduction
Computer performance depends on:
– Processor performance
– Memory system performance
Memory System Performance
Analysis
Evaluation Primary Memory
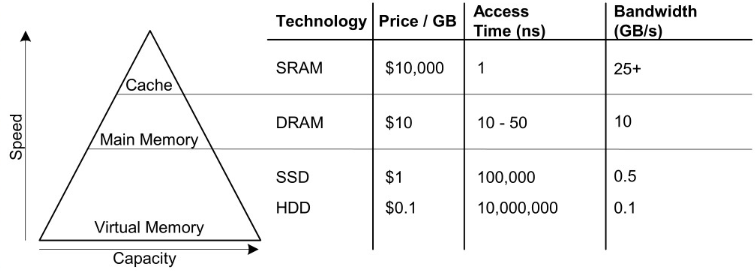
–3 Key characters :Capacity, speed and price
• Price per bit, P=C/S (C—price of memory,S—capacity(bits))
• Larger capacity, faster speed --> higher price
Multi-layered Memory
Memory
speed: lower than CPU
capacity: falls behind the need of software.
To solve this
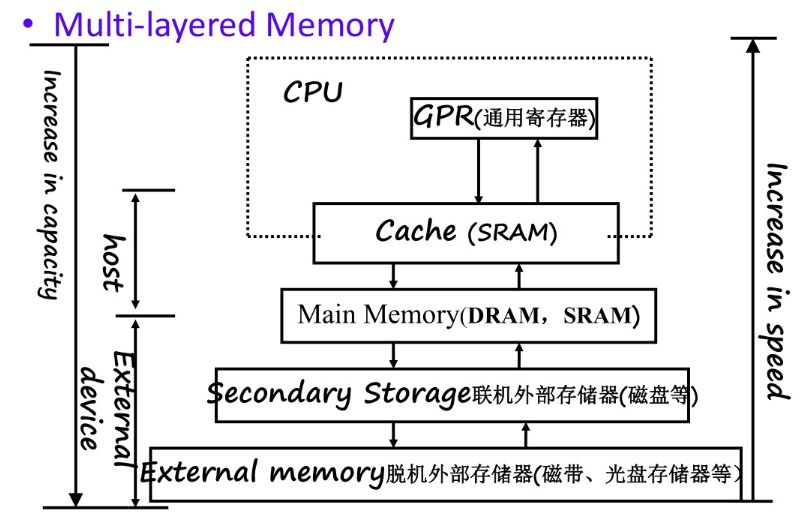
Memory Hierarchy
Locality
Temporal Locality
– Locality in time
– If data used recently, likely to use it again soon
– How to exploit: keep recently accessed data in higher
levels of memory hierarchy(cache)
Spatial Locality
– Locality in space
– If data used recently, likely to use nearby data soon
– How to exploit: when access data, bring nearby data
into higher levels of memory hierarchy too(cache)
cache
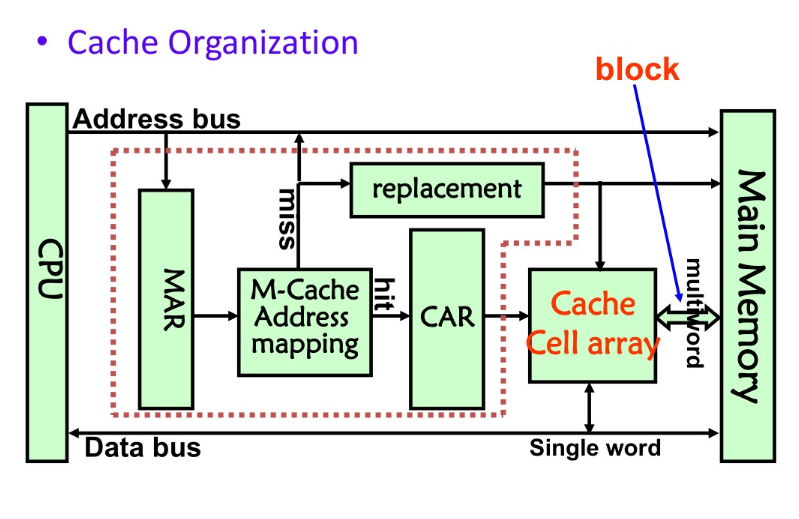
MAR: memory address register
CAR: cache address register
Hit: data found in that level of memory hierarchy
Miss: data not found (must go to next level)


Memory Performance
Tc : cache access time
Tm : the time spent for transferring a main memory block to the cache
Ta : average access time
Average memory access time (AMAT): average time for processor to access data

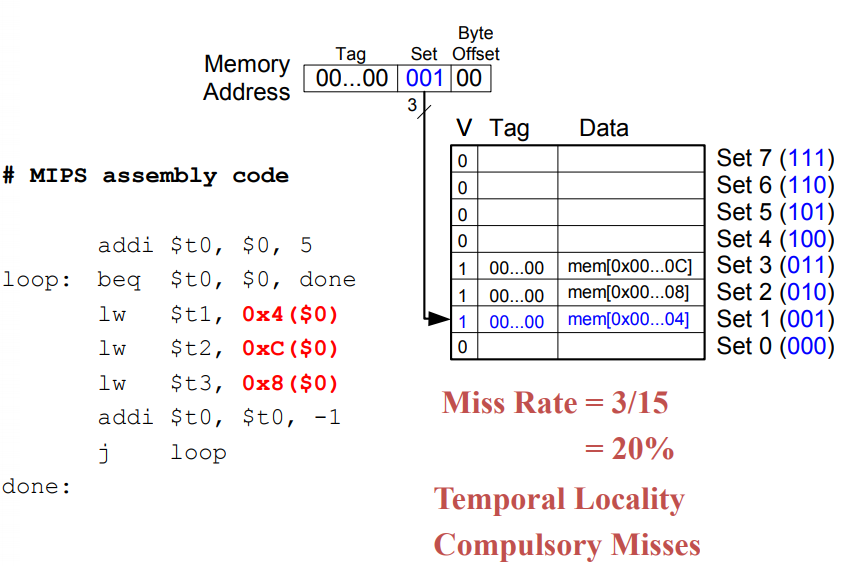
Cache Terminology

Direct Mapped Cache Hardware
one bit for v (if the roll is empty , v=0)
set number : locate the role
N-Way Set Associative Cache
Each memory address still maps to a specific set, but it can map to any one of the N blocks in the set.
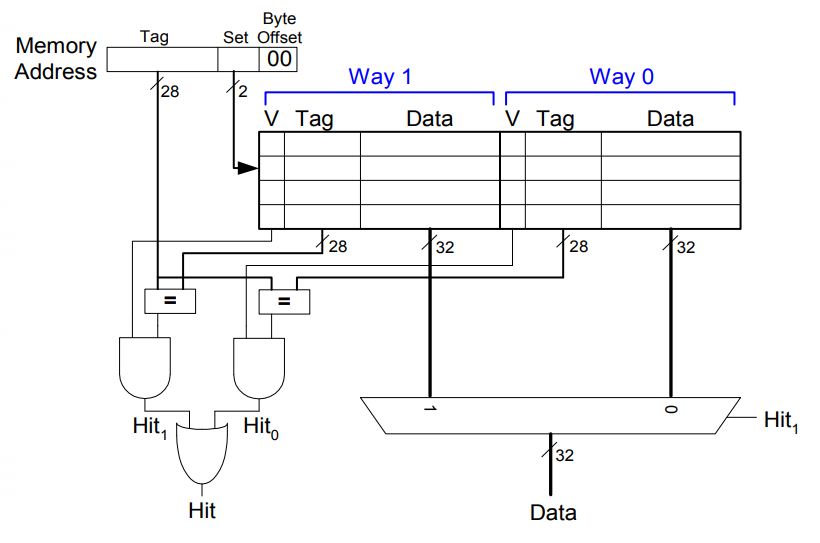
Full Associative Cache
Conflict can be further reduced
Larger blocks reduce compulsory misses through spatial locality
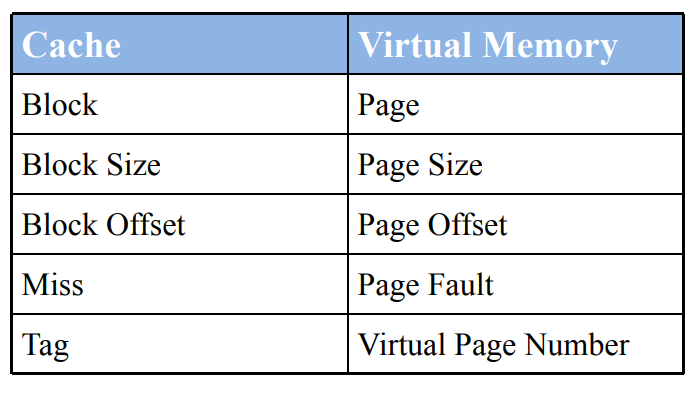
Virtual Memory
Virtual memory is much bigger than physical one.
Virtual Address
-
Programs use virtual addresses
-
Entire virtual address space stored on a hard drive
-
Subset of virtual address data in DRAM
-
CPU translates virtual addresses into physical addresses (DRAM addresses)
-
Data not in DRAM fetched from hard drive
Memory Protection
– Each program has own virtual to physical mapping
– Two programs can use same virtual address for different data
– Programs don’t need to be aware others are running
– One program (or virus) can’t corrupt memory used by another
-
Page size : amount of memory transferred from hard disk to DRAM at once
-
Address translation : determining physical address from virtual address
-
Page table: lookup table used to translate virtual addresses to physical addresses
-
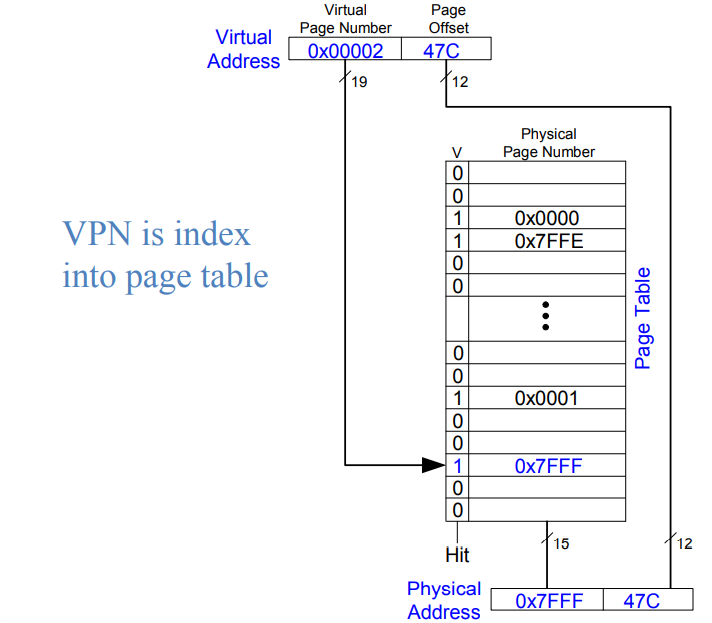
Virtual page number 的最后一位是2,所以在表中从下往上对应2位置(0,1,2…)
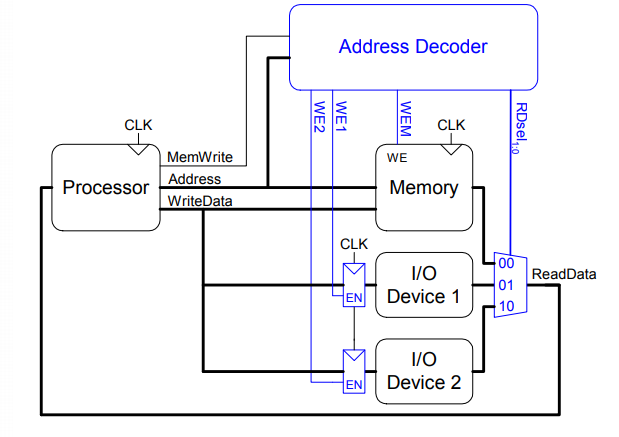
Memory-Mapped I/O
Hardware
- Address Decoder
- I/O Registers
- ReadData Multiplexer