Chapter 4 Requirements Specification
Architectural prerogatives
Architectural design
Design
- detailed
- architectural
Architectural model
- hierarchical layers
- restrictions on object inter-communications to minimize dependencies
MVC
- Model : represent data objects
- View : represent user interface(UI) objects
- Controller: represent mouse and keyboard events
J2EE
- The users communicates with the system from the client server
- EIS tier(also called Resource tier) is any persistent(持久性) information delivery system
- The users access the application via the Presentation tier (Web tier)
- Business tier contains application logic
- Integration tier establishes and maintains(维护) connections to data sources
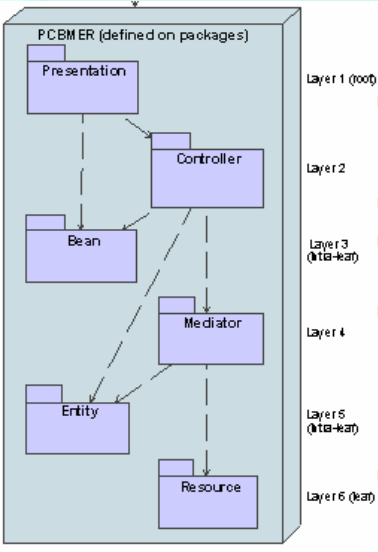
The Core PCBMER framework
Presentation represents the screen and UI objects
Bean represents the data classes and value objects
Controller represents the application logic
Entity contains classes representing business objects
Mediator manages business transactions, enforces business rules, instantiates business objects in the Entity layer, and in general manages the memory cache of the application
Resource is responsible for all communication with external persistent data sources
Architectural principles
DDP – downward dependency principle
- Higher PCBMER layers depend on lower layers
- lower layers should be designed to be more stable
UNP – upward notification principle
- Upward communication that minimize object dependencies
- Lower layers rely on interfaces and event processing to communicate with objects in higher layers
NCP – neighbor communication principle
- Objects can communicate across layers only by using direct neighbors
- chains of message passing
APP – acquaintance(熟人) package principle
EAP – explicit(显式的) association principle
CEP – cycle elimination(淘汰) principle
CNP – class naming principle
State Specifications
- Model of data structures
- Static view on the system
- Class operations left out in initial specs
- Emphasis on entity classes (‘business objects’)
Modeling classes
- Cornerstone(基石) of OO development
- Iterative and incremental process
- Case tool
- For collaborative development
- For personal productivity otherwise
Discovering classes
- Noun phrase
- Common class patterns
- From candidate classes from the classification theory of objects
- 😢 Only loosely bound to user requirements
- 😢 Possible naming misinterpretations(命名误解)
- Use case driven
- Function driven
- Relies on the completeness of use case models
- CRC
- class, responsibilities,collaborators
- Mixed
- Use elements of all four previous approaches


