Chapter 2 Requirements Determination
🍕From business process to solution envisioning
IT Solution
- Implementation of a business process
BPMN
Business Process Modeling Notation
UML activity diagrams
Goal: Map these notations to an executable language
BPMN categories of modeling events
- Flow objects
- Events
- Activities
- Gateways
- Connecting objects
<img src="/images/typora/image-20201229204732957.png"style=“zoom:80%;” />
-
Pools (Swim lanes)
A pool represents a business entity (participant) in a process.
❗️ the sequence flow may not cross the boundary of a pool
-
Artifacts
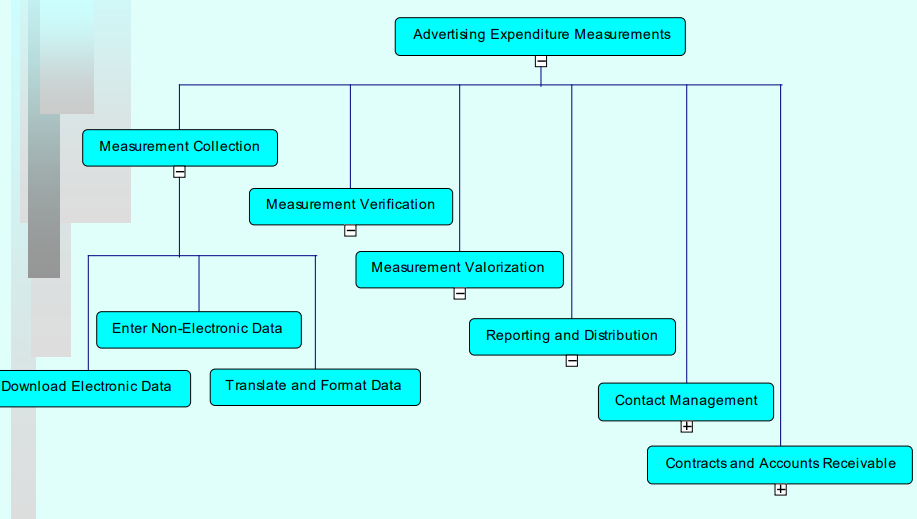
Process hierarchy modeling
-
sub-processes
A process may contain other processes
-
task
An atomic activity within a process
-
process hierarchy(等级制) diagram
- A business process can be performed manually or an automated service
- A process has at least one input flow and one output flow
- A process can be atomic or composite
-
Solution envisioning
-
a business value-driven approach to delivering an IT service
-
makes a close connection between business and IT stakeholders and integrates(整合) business strategy methods and software development capabilities.
-
Three “E-s” (efficiency, effectiveness, and edge)
-
Three phases
- Business capability exploration
- Solution capability envisioning
- Software capability design (outcome : software capability architecture)
-
Three distinct implementation strategies
- Custom development
- Package-based development
- Component-based development
🍕Requirements Engineering
Products
Primary outcome is a requirements specification
Secondary outcome is a usually system and software acceptance test criteria
Why is RE important
- Helps earlier detection of mistakes
- Forces clients to articulate and review requirements
- Enhance communications between participations
What happens if Requirements are wrong
- System may be delivered late and cost more.
- Customers and end-users are not satisfied
- System may be unreliable in use
Functional Requirements
- Requirements (or capabilities) for functions must be performed by the system
- Primary focus of most requirements activities
Non-Functional Requirements
- System properties and constraints
- More critical than functional requirements
- NFR Sources
- Product requirements
- Process requirements
- External requirements
Verifiable
❗️ Imprecise requirements cannot be verified
NFR should be a measurable statement
Requirements Engineering Process
- Requirements Elicitation(启发) and Analysis
- Requirements Specification
- Requirements Validation(验证方式)
- Requirements Management
🍕 Requirements Elicitation
Requirements elicitation principles
System development is motivated by a problem
- Aim: to understand the problem clearly
Requirements elicitation activities
- Analyzing the problem
- Identifying requirements sources
- Eliciting requirements from these sources
Requirements elicitation techniques
- Challenges
- Stakeholders and users may not be able to describe their tasks well
- Requirements conflict
- Implicit(隐式) requirements
Interviews
- Prepare questions in advance
- Suggest ideas & alternatives
Workshops
- Structured meeting
- formal roles
- clear goals
- Multiple stakeholders
- resolve conflicting requirements
- gather board system usage
Focus Groups
- Less structure
- Exploratory(探索性) discussion
- Broad stakeholder representation
- Gather broad-based ideas
Observations
- Observe how users perform their tasks
- Users often cannot describe everything they do
- Time consuming
Questionnaires
- Inexpensive and easily administered to remote sites
- Collect data from many users
- May feed into interviews or workshops
- 😢 Good questionnaires difficult to write
- 🍰 Good Questionnaire
- Answer options for all possibilities
- Answer choices mutually exclusive(互斥)
- Avoid phrasing that implies a correct answer
- Closed questions for statistical analysis
- Open questions to gather ideas
- Short
Independent Elicitation Techniques
Discover information on your own
System interface analysis
- Look at other systems’ functionality
- Data exchange (including formats & validation(验证) rules)
- Services
User interface analysis
- Study existing systems
Document analysis
- Business process descriptions
- Existing system documentation
- Industry standards or legislation
- Gain understanding of domain or system
Product of elicitation phase
- Requirements documentation including a requirements definition
- May use pre-defined requirements document template
- IEEE, ISO,…
- May use less formal documentation and tools
- User Stories, Jira…
🍕 Requirements negotiation and validation
Frequently done in parallel with requirements elicitation
📁 Inseparable from the production of requirements document
- negotiation starts from the draft requirement doc
- validation reviews and approves the doc
🌵 Requirements dependency matrix
- Conflict & Overlap
Requirements risks and priorities
- Risk analysis identifies requirements that are likely to cause development difficulties
- Prioritization(优先次序) allows easy re-scoping of the project when faced with delays
Risk Categories
- Technical
- Performance
- Security
- Database integrity(数据库完整性)
- Development process
- Political
- Legal
- Volatility (挥发性)
Requirements Management
Requirements identification and classification
- Natural language statements
- Identification and classification scheme
- Unique identifier
- Sequential number with document hierarchy (文件等级制)
- Sequential number with requirement’s category (需求类别)
Requirements hierarchies
🍼 Parent-child relationships
Reflect varying abstraction levels
-
…
1.1…
1.2…
1.3…
Change management
Downstream cost of change
- Strong management policies
- document change requests
- assess change impact
- effect the changes
⚠️ Requirements changes should be stored and tracked by a software configuration management tool
Requirements traceability
suspect trace : After change to any element in a traceability relationship
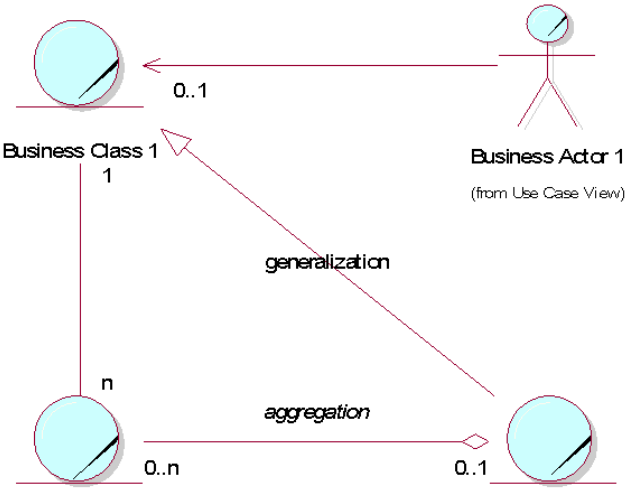
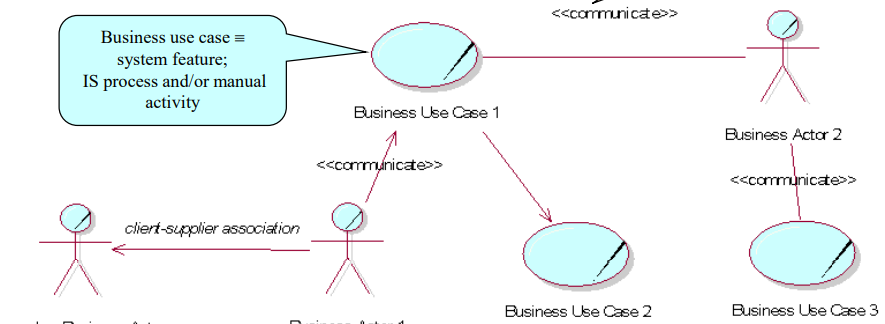
Requirements business model
Context diagram (System scope)

Business Use case diagram(function requirements)
Business class diagram (data requirements)